Feed
Please login to create a post.
2025-10-30 17:46:57
Fix for unreadable junk characters in Microsoft 365 mail usage reports
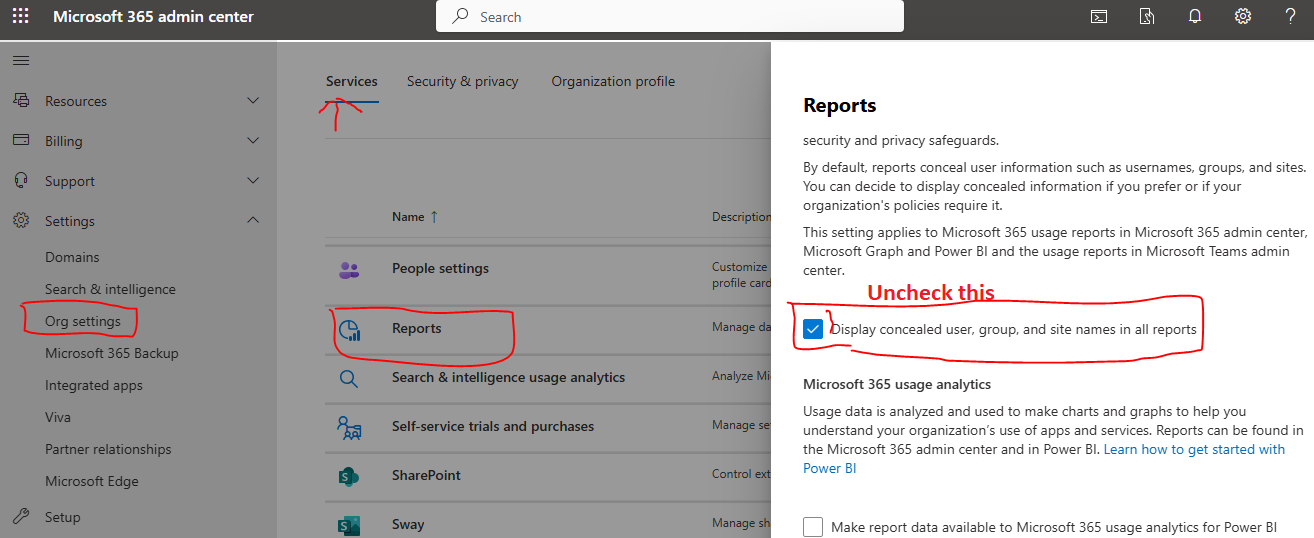
Recently, while checking mail usage in Microsoft 365, we noticed that instead of showing proper email addresses, the report displayed unreadable junk characters.
This usually happens because user details are concealed by default for privacy reasons.
To fix it
1 Go to Microsoft 365 Admin Center
2 Navigate to Settings then Org Settings
3 Select Services tab and open Reports
4 Uncheck this option Display concealed user group and site names in all reports
Once enabled you will see proper usernames and email addresses in your reports.
2025-10-01 08:39:59
VMWare # Many of VMware Admin had faced a situation.
VM running on vSAN failed to power on with errors showing insufficient resources and component absent. This occurred after one of the ESXi hosts in the cluster was down for several hours.
On investigation we found the root cause. vSAN objects were marked absent because the host holding one replica had been offline for more than 60 minutes. With an FTT=1 policy, quorum requires at least 2 of 3 components. As quorum was lost, the VM could not power on.
Steps we performed to resolve the issue:
1. Checked vSAN health using
esxcli vsan health cluster list
2. Verified which components were marked absent.
3. Attempted to bring the down host back online as quickly as possible.
4. In case the host is permanently unavailable, we prepared to add a new host and configure a new disk group.
5. Triggered a vSAN rebuild so that missing components could be recreated and quorum restored.
6. Once quorum was available, we retried powering on the VM and it came online successfully.
Key takeaway. Always design vSAN clusters with a minimum of 3 hosts when using FTT=1 to ensure quorum and availability.
2025-10-01 08:21:00
VMWare # Last week issue reported where the vCenter Server Appliance UI was not opening and the vSphere client was not loading. This impacted day to day management of the VMware environment.
We resolved the issue by performing the following steps:
1. SSH into the vCenter Server Appliance using the root account.
2. Stopped all services using
service-control --stop --all
3. Restarted all services using
service-control --start --all
4. Checked the overall health of the appliance by running
df -h
This helped to confirm if any of the disk partitions were full.
5. Cleared unnecessary log files and rotated old logs where required to free up space.
Monitored the service startup and confirmed that the UI was accessible again.
After these steps the vSphere client was loading normally and operations were restored.
2025-10-01 08:11:44
VMWare # Recently we faced an issue on one of our ESXi hosts where high CPU and memory usage was reported. This led to performance alarms and noticeable slowness for end users.
We followed the below troubleshooting and resolution steps to address the problem:
1. Logged into vSphere and checked which virtual machines were consuming high CPU and memory.
2. Verified whether the resource consumption was genuine or caused by runaway processes inside guest operating systems.
3. Performed manual VM migrations to other hosts in the cluster since DRS was not enabled.
4. Optimized resource allocation for some virtual machines by adjusting CPU and memory reservations where required.
5. Planned to enable DRS to allow automatic balancing in the future and considered adding additional hardware resources for scalability.
This helped stabilize performance and cleared the alarms on the host.
2025-09-07 05:16:53
VMWare # NSX-T = VMware NSX-Transformers (officially “NSX-T Data Center”)
________________________________________
Simple Explanation
NSX-T is VMware’s software-defined networking (SDN) platform.
It lets you create, manage, and secure networks entirely in software — no need to rely on physical network gear for every change.
Think of it as the “network virtualization” part of SDDC.
________________________________________
Key Points about NSX-T
1. Multi-Platform
o Works not only with VMware vSphere (ESXi) but also KVM, bare metal, containers (Kubernetes), and public clouds.
o This is why VMware created NSX-T — NSX-V worked only with vSphere.
2. Core Features
o Logical Switches – Software-based networks for VMs/containers
o Logical Routers – Routing between virtual networks without physical routers
o Distributed Firewall – Security rules applied at the VM’s virtual NIC level
o Micro-Segmentation – Isolate workloads without changing physical network
o Load Balancing, VPN, NAT – All done in software
3. Use Case
o You can create a new network segment in seconds without touching a single switch or cable.
o Security rules follow the VM even if it moves to another ESXi host via vMotion.
________________________________________
Example
Without NSX-T:
• To create an isolated network for testing, you’d reconfigure VLANs on physical switches and update firewalls.
With NSX-T:
• You open the NSX-T Manager, click “Add Segment”, and the network is ready — no physical changes needed.
________________________________________
Purpose:
• Faster network provisioning
• Stronger, granular security
• Multi-cloud and container-ready networking
• Fits into SDDC as the network virtualization layer
2025-09-02 15:29:44
Boost Your Productivity with One-Click Access
Managing multiple applications every day can be time-consuming—searching, launching, and switching between different user IDs.
In this video [link below], I explain a simple yet powerful way to:
* Launch all your daily-use applications from one window
* Save time by avoiding repeated searches
* Even start apps with different user IDs when required
This approach makes your workflow faster, more efficient, and hassle-free. Perfect for IT professionals, admins, and anyone juggling multiple tools daily!
👉 Watch here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UXpv1NE-ZJ4
2025-09-02 12:04:57
Sometimes people mistakenly use "Gen1" and "Gen2" when talking about VMware, usually in the context of importing VMs from Hyper-V or nested virtualization. In Hyper-V "Gen1" and "Gen2" are Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machine generation types.
Here’s the breakdown:
In Hyper-V
Generation 1 (Gen1)
* Emulates legacy BIOS-based boot (MBR partition).
* Uses IDE controllers for the virtual hard disks.
* Supports older guest operating systems (e.g., Windows Server 2008, 2012).
* Doesn’t support Secure Boot or UEFI features.
* Better for compatibility when the guest OS doesn’t support UEFI.
Generation 2 (Gen2)
* Uses UEFI firmware (GPT partition support).
* Boots directly from SCSI virtual disks.
* Supports Secure Boot, PXE boot via synthetic network adapter.
* No floppy drives or legacy hardware.
* Recommended for newer OS versions (Windows Server 2012 R2 and later).
In VMware
VMware does not have "Gen1" or "Gen2" labels, but the concept maps like this:
Gen1 ===== VM configured with BIOS firmware (in VM options).
Gen2 ===== VM configured with EFI / UEFI firmware.
When creating or editing a VM in VMware:
* BIOS Mode → Use when migrating older OS that require MBR boot.
* EFI / UEFI Mode → Use for modern OS, Secure Boot, and GPT partitioning.
When to choose in VMware:
Use BIOS if:
* OS only supports legacy BIOS boot.
* You’re importing a Gen1 Hyper-V VM.
Use UEFI if:
* OS supports it (modern Windows/Linux).
* You want Secure Boot or GPT.
* You’re importing a Gen2 Hyper-V VM.
2025-09-02 06:33:59
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4MLQWqkRthg
This video is all about PowerShell script to perform basic task for a system engineer or even for helpdesk.
Todays script is to find latest hotfix / patch got installed, to find any changes happened on OS level and any network connectivity issue like server or workstation was not reachable in between or went offline.
the script will check in event logs and shared the output in text file.
=======================================
if you need these scripts then please visit my website - "dvirus.in" or sent me email on dattam@dvirus.in.
2025-09-01 07:09:27
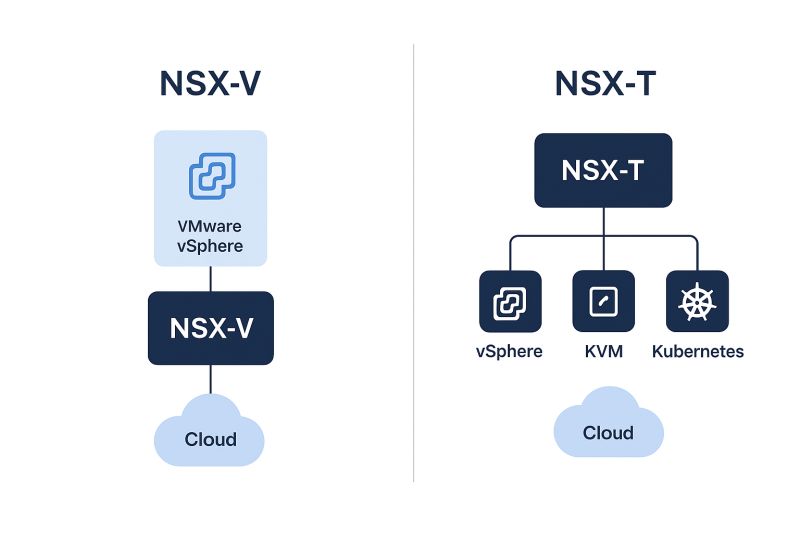
VMWare # What is NSX-V and NSX-T in VMware?
VMware NSX is a network virtualization and security platform that brings networking and security functions closer to the application. Over the years, VMware introduced two major versions – NSX-V and NSX-T.
NSX-V (vSphere NSX)
NSX-V was tightly integrated with VMware vSphere environments. It relied on the VMware vCenter Server and vSphere Distributed Switches. This meant it was great for organizations running only VMware vSphere but had limitations when working with multi-hypervisor or cloud-native workloads.
NSX-T (NSX Transform)
NSX-T is the next-generation network virtualization solution from VMware. It is designed for a multi-cloud and multi-hypervisor world. NSX-T supports not only vSphere but also KVM, containers like Kubernetes, and public cloud platforms. It provides advanced features like distributed routing, micro-segmentation, and security for both traditional and modern applications.
The Key Difference
NSX-V is vSphere-specific and cannot run outside of a VMware ecosystem.
NSX-T is platform-agnostic, making it more flexible and future-proof for organizations adopting hybrid cloud, containers, and multi-hypervisor strategies.
With NSX-T, VMware has shifted focus to support modern application architectures, offering enterprises more scalability, agility, and security across diverse infrastructures.